Nurses interested in working in the UK are required to demonstrate their English language proficiency by clearing OET.
Read about the OET test and how we can help you pass the OET listening, reading, speaking and writing modules. Or learn about the OET test here.
Most applications are made online through the university website. You will have to send supporting documents, such as exam transcripts and pay an application fee.
Different courses may have different application processes. For example, there may be different deadlines, need for previous qualifications, only having certain intake dates and etcetera.
Admission to Singaporean universities is also increasingly competitive as the number of foreign students allowed to study in different universities is being limited by the government.
You will be issued an in-principle approval (IPA) letter upon acceptance from your university, which will include your entry visa. Within two weeks of receiving your IPA letter you will need to obtain a Student’s Pass, issued by the Immigration & Checkpoints Authority (ICA). The pass covers the duration of your course. You can apply for one through the Students Pass Online Application & Registration System (SOLAR), within 1 to 2 months before the start of your course. On arrival in Singapore you’ll have to produce documents including but not limited to your passport, disembarkation/embarkation card and a medical report, at a pre-booked appointment with the ICA. A Student’s Pass is unnecessary if you hold a Dependant’s Pass or an Immigration Exemption Order
Singapore is one of the most expensive cities in the world so it’s worth seeking out additional sources of cash to help with your finances. Over 50% of international students in Singapore receive financial aid. Contact your university to find out more about the financial aid they offer. Researching for government support is also recommended at the Ministry of Education (MOE) Singapore – Financial assistance. You may also be eligible for scholarships, for example, ASEAN scholarships are for students who originate from a member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations. International students without scholarships are eligible for reduced tuition fees. However, that will come with a bond to work in the country for at least three years after the course. Alternatively, repayable tuition fee loans are available to those without scholarships. These are worth up to 90% of the fees payable by Singaporean citizens for the same course. To assist with school fees, you can work part time while studying and full-time during holidays, pending your university’s approval.
In Poland, there are only 11 fields of study that offer long-cycle programs:
This Master’s degree program lasts 4.5 to 6 years and leads to the professional title of Master (magister).
To obtain this degree, you must earn 270-360 ECTS credits.
Otherwise known as doctoral-level programs. This degree normally lasts 3 to 4 years and it is accessible after graduating from a Master’s degree program. All doctoral colleges are tution-free, also for foreigners.
A Master’s degree program lasts 1.5 to 2 years and follows the first cycle studies. After graduation, you will gain the professional title of Master (magister or an equivalent degree depending on the course profile). To obtain this degree, you must earn 90-120 ECTS credits.
After getting your Master’s degree you are free to enter a doctoral program (third-cycle studies).
Open to holders of an upper secondary school certificate (Matura certificate) or an equivalent entitling the holder to enrol in such programs in Poland. Additional entrance examinations may be conducted by HEIs only if this is necessary to assess knowledge or skills that are not assessed by the Matura examination or the applicant holds an upper secondary school certificate obtained abroad.
After finishing the first-cycle studies (3 to 4 years) you get the professional title of a licencjat or inżynier (Engineer, in the field of engineering, agriculture or economics). This is the Polish equivalent of the Bachelor’s degree. To obtain a licencjat degree, you must earn 180-240 ECTS credits during your studies.
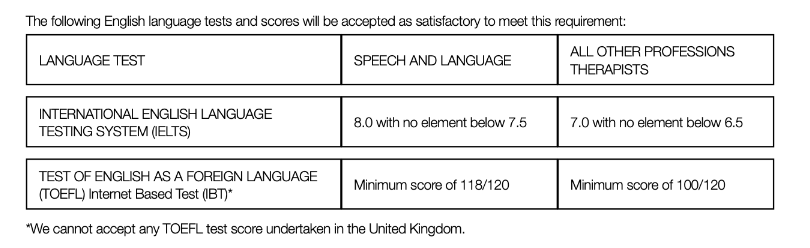
Speech and language therapists have higher English proficiency requirements than other professionals.
The Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC) is the body that regulates most allied health professionals (AHPs) in the UK. The exception are osteopaths who need to register with the General Osteopathic Council (GOsC). The HCPC and GOsC set standards of professional training, performance and conduct and hold a register of health professionals who meet the registration standards. Registration requires qualification verification, history of professional experience, background check, scrutiny fee (£539.65 one off non-refundable application fee).
If you need to apply for a visa, learn about the eligibility criteria and visa application process by clicking here.
Check out the education, practice and registration requirements for nurses looking to work in the UK. (more…)
Find out about the certificate of entitlement and if you qualify for the right of abode in the UK.
Nurses interested in working in the UK are required to demonstrate their English language proficiency by clearing either IELTS or OET.
Read about the IELTS test and how we can help you pass the IELTS listening, reading, speaking and writing modules. Or learn about the OET test here.
You will need to apply for registration with the Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) for nursing jobs in the UK. Find out about the application process for overseas nurses by clicking here
Since 1 April 2006, all doctors working in general practice in the NHS in the UK (other than doctors in training such as GP registrars) are required to be on the GP Register. This requirement extends to locums.
If you have not completed the UK GP Certificate of Completion of Training programme you will need to apply for a Certificate of Eligibility for General Practice Registration (CEGPR), which will then enable you to be entered on the GP Register.
All consultants (other than a locum consultant appointment) must be on the specialist register of the General Medical Council (GMC). To be eligible to apply for specialist registration with the GMC, doctors must have successfully completed a GMC-approved training programme and been granted one of the following certificates:
Doctors who have not completed a full GMC-approved training programme and wish to have their training, qualifications and experience assessed for eligibility for entry onto the specialist register must make an application under The General and Specialist Medical Practice Order for a CESR. It is not possible to hold specialist registration without also holding full registration.
Full registration enables doctors to work in any form of professional medical practice in the UK, provided they hold a licence to practise. Doctors must, however, also hold specialist registration to take up a consultant post (other than a locum consultant post); and those wishing to work as GPs must be on the GP register.
Doctors qualifying from outside the UK may be eligible to apply directly for full registration if they hold an acceptable primary medical qualification and have completed a period of postgraduate clinical experience (internship).
A doctor will need to provide documentary evidence to support their application. Only original documents can be accepted. To complete the process, all doctors must visit the GMC in person to undergo a pre-registration identity check. A photograph of the doctor will be taken and this will be made available to employers so they can be assured of the doctor’s identity.
UK graduates and IMGs who are new to full registration and taking up a new job, or restoring their names to the register after a prolonged absence from practice, are required to work within an approved practice setting (APS) as assessed by the GMC as suitable for doctors new to full registration. The GMC recommends that EEA graduates ensure that they also work in an APS when they first take up employment in the UK under full registration. Most NHS employers will have approved practice setting status.
The purpose of the APS system is to provide public protection by requiring doctors new, or returning, to full registration in the UK to work within a system with appropriate supervision and appraisal arrangements or assessments.
Provisional registration (alongside a license to practice) only allows newly qualified doctors to undertake an approved Foundation Year 1 post. The law does not allow provisionally registered doctors to work in any other type of post. On successful completion of Foundation Year 1, you will be able to apply for full GMC registration.
Provisional registration is available to doctors with the following nationality, rights and qualifications:
There are many schemes offering training posts to overseas doctors. The most well-known is the Medical Training Initiative, run by the Academy of Medical Royal Colleges. Recruitment focuses of suitably qualified, overseas, post graduate medical specialists (who have passed Part 1 membership exams for the Royal College of Physicians). Successful applicants are recruited for a fixed period of training in the UK before returning to their home healthcare system.
The British Association of Physicians of Indian Origin (BAPIO) offer post graduate training programmes in association with Health Education England. The training scheme is offered to applicants who do not have relevant postgraduate training in India. BAPIO offers a route to gain both membership and fellowship in various specialties + leadership training through a combination of posts in both India and the UK for a fixed term (2-4 years).
Most training schemes operate on a time-limited Tier 5 vias (which only lasts 2 years) where Doctors must return to India at the end of their training.
The PLAB exam tests the applicant’s knowledge and skills to ensure that they are as qualified as a UK 2nd year Foundation doctor.